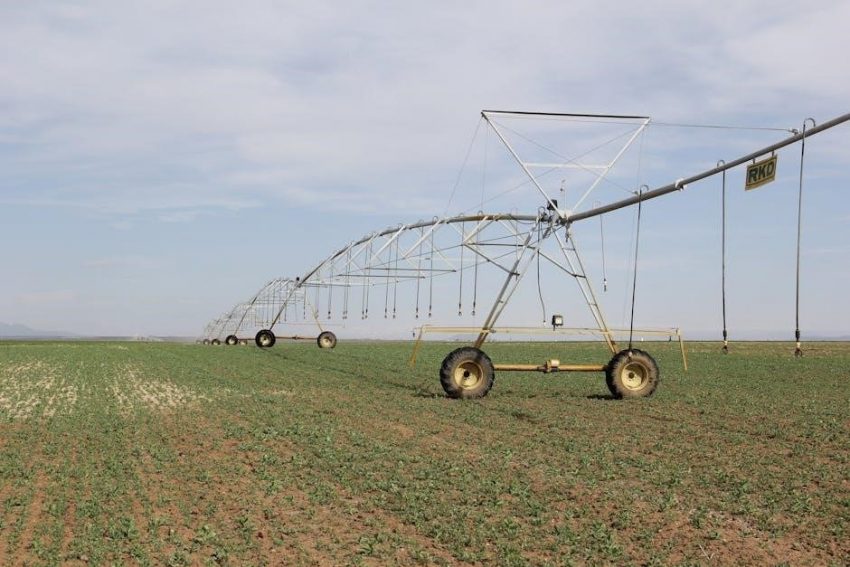
Sprinkler irrigation system design enhances water conservation and crop production efficiency by distributing pressurized water uniformly across fields, adaptable to various terrains and soil types for optimal agricultural use.
Overview of Sprinkler Irrigation Systems
Sprinkler irrigation systems involve pressurized water distribution through a network of pipes and sprinklers, mimicking natural rainfall. These systems are highly adaptable to various field shapes, soil types, and terrains, making them suitable for diverse agricultural and landscape applications. Key components include pumps, mainlines, laterals, and sprinkler heads, which work together to deliver water uniformly. They can be permanent, semi-permanent, or portable, offering flexibility for different cropping systems. Sprinkler systems enhance water conservation, reduce labor, and improve crop yields by ensuring precise water application.
Importance of Efficient Irrigation System Design
Efficient sprinkler irrigation system design is crucial for optimizing water use, reducing runoff, and ensuring uniform water distribution. Proper design minimizes energy costs by reducing pressure losses and optimizes water application rates. It also enhances crop yields by maintaining soil moisture at ideal levels. Efficient systems reduce labor costs and environmental impact by preventing overwatering and deep percolation. Well-designed systems ensure long-term sustainability by conserving water resources while maintaining high agricultural productivity.

Types and Configurations of Sprinkler Irrigation Systems
Sprinkler irrigation systems include center pivot, permanent, semi-permanent, portable, and solid set configurations, each suited for specific agricultural needs and field conditions to ensure efficient water distribution.
Center Pivot Sprinkler Irrigation System
A center pivot sprinkler irrigation system features a rotating lateral supported by towers, anchored at a central pivot point, irrigating circular fields. It uses end guns and swing lines for larger areas, ensuring uniform water distribution. This system is highly efficient, reducing evaporation and runoff, and is suitable for various terrains and crops. Its design minimizes labor and optimizes water use, making it a popular choice for modern agricultural irrigation needs.
Permanent, Semi-Permanent, and Portable Systems
Permanent sprinkler systems feature buried main and lateral lines, offering durability and reduced maintenance for large-scale irrigation. Semi-permanent systems combine fixed mainlines with portable laterals, balancing flexibility and cost. Portable systems, with movable main and lateral lines, are ideal for small or irregularly shaped fields. Each design caters to specific agricultural needs, ensuring efficient water distribution while accommodating varying budgets and operational requirements.
Fixed or Solid Set Sprinkler Irrigation System
A fixed or solid set sprinkler irrigation system features permanent installations with sufficient piping and sprinkler heads to cover the entire field without moving laterals. This setup is ideal for rectangular areas, ensuring uniform water distribution and eliminating the need for system relocation. It minimizes labor costs and operational complexities, making it a practical choice for consistent irrigation needs. The design ensures optimal water application, reducing runoff and enhancing soil moisture retention for healthier crop growth.

Design Considerations for Sprinkler Irrigation Systems
Designing sprinkler systems requires balancing nozzle size, operating pressure, sprinkler spacing, and soil infiltration rates to ensure efficient water distribution and prevent runoff or overwatering challenges.
Key Factors in Sprinkler System Design
Nozzle size, operating pressure, and sprinkler spacing are critical for uniform water distribution. Soil infiltration rates and crop water requirements must be considered to avoid overwatering. Pressure losses in pipelines and fittings impact system efficiency. Hydraulic calculations ensure proper water flow and pressure distribution across the field. Matching system components to soil type, field layout, and water availability optimizes performance. Proper design balances water application rates with soil absorption capacity to maximize irrigation efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
Nozzle Size, Operating Pressure, and Sprinkler Spacing
Nozzle size determines water flow rate and distribution pattern, while operating pressure affects spray uniformity and reach. Proper sprinkler spacing ensures adequate coverage without overlap. Soil infiltration rates influence nozzle selection to prevent waterlogging. Balancing these factors ensures efficient water application and minimizes waste. Optimal spacing and pressure settings are calculated based on field topography and crop requirements. Correct configuration enhances water distribution uniformity, ensuring consistent soil moisture levels and promoting healthy plant growth. Proper design avoids overwatering and reduces environmental impact.
Soil Infiltration Rate and Water Application Rates
Soil infiltration rate dictates how quickly water penetrates the soil, influencing irrigation system design. Water application rates must align with infiltration capacity to avoid runoff and ensure efficient moisture delivery. Higher infiltration rates require adjusted application rates to prevent waterlogging. Proper balancing ensures optimal soil moisture levels, promoting healthy plant growth. Designing systems to match soil characteristics prevents overwatering and reduces environmental impact. Accurate calculations of infiltration and application rates are critical for sustainable and effective irrigation practices.
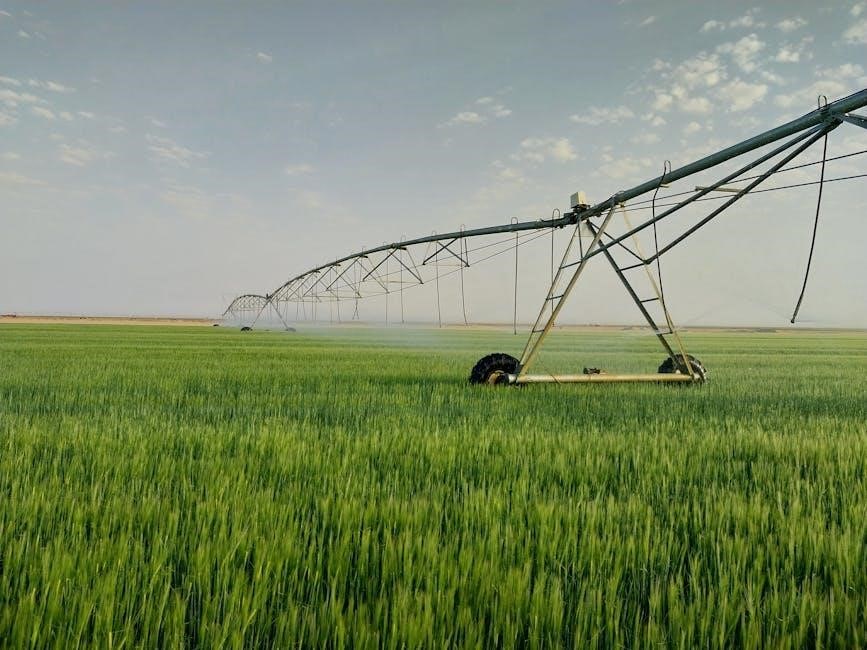

Water Supply and Pressure Requirements
Water supply and pressure requirements ensure efficient sprinkler system operation, with a reliable source and adequate pressure to meet flow rate demands, minimizing losses and optimizing performance.
Source of Water for Irrigation Systems
The source of water for irrigation systems is a critical factor in design, ensuring sustainability and reliability. Common sources include groundwater, surface water, recycled water, and rainwater. Groundwater is often preferred for its consistent supply, while surface water may require treatment. Recycled water offers environmental benefits but needs quality assessment. Rainwater harvesting is eco-friendly but limited in capacity. Evaluating water availability, quality, and cost is essential to select the most suitable source, ensuring long-term system efficiency and crop productivity.
Pressure Losses in Pipelines and Fittings
Pressure losses in pipelines and fittings are critical factors in sprinkler irrigation system design. Friction losses occur due to water flow, pipe material, length, and diameter. Fittings like valves, elbows, and couplers also contribute to pressure drop. Accurate calculations are essential to ensure sufficient pressure at sprinkler heads for uniform water distribution. Neglecting pressure losses can lead to inadequate irrigation coverage, reduced efficiency, and system underperformance. Proper pipe sizing and material selection help minimize losses, ensuring optimal system operation and water application rates.
Hydraulic Calculations for System Design
Hydraulic calculations are essential for ensuring a sprinkler irrigation system operates efficiently. These calculations determine flow rates, pressures, and pipe sizes based on factors like nozzle size, sprinkler spacing, and water source. Accurate hydraulic analysis ensures that water is distributed uniformly across the field, maintaining optimal pressure at each sprinkler head. Proper calculations also prevent energy losses and overwatering, ensuring the system meets crop water requirements while conserving resources. This step is critical for designing a reliable and high-performing irrigation system tailored to specific agricultural needs.

System Layout and Sprinkler Spacing
System layout and sprinkler spacing are crucial for uniform water distribution, ensuring efficiency and preventing overwatering. Proper design tailors these elements to field geometry and crop needs.
Layout of Sprinkler Irrigation System
The layout of a sprinkler irrigation system is tailored to the field’s geometry and soil type, ensuring efficient water distribution. It involves positioning main and lateral pipes strategically to deliver water to sprinklers. The design must account for the water source, pressure requirements, and terrain to achieve uniform coverage. Proper layout minimizes overlaps and gaps, ensuring even water application. This step is critical for optimizing irrigation efficiency and crop productivity, making it a cornerstone of effective system design.
Importance of Sprinkler Spacing and Overlapping
Proper sprinkler spacing and overlapping are crucial for achieving uniform water distribution, ensuring that all areas of the field receive adequate irrigation. Overlapping prevents dry spots and ensures complete coverage, while correct spacing avoids excessive water application. Uniformity is key to crop health and water conservation. Improper spacing can lead to under-watering or over-watering, reducing efficiency and increasing runoff. Optimal spacing and overlap maximize system performance, ensuring resources are used effectively and crop yields are maintained at their highest potential.
Uniformity of Water Distribution
Uniformity of water distribution is critical for ensuring consistent irrigation across the field. It prevents under-watering or over-watering, which can harm crops and waste resources. The uniformity distribution coefficient measures how evenly water is applied. Proper sprinkler spacing, nozzle selection, and system design are essential for achieving high uniformity. Non-uniform irrigation can lead to dry spots and reduced crop yields. Optimal design ensures water is delivered consistently, promoting healthy plant growth and efficient water use. Uniformity is a key indicator of system performance and agricultural productivity.

Evaluation of System Uniformity and Efficiency
Evaluation of system uniformity and efficiency involves assessing water application rates, distribution patterns, and overall performance. It ensures optimal irrigation and resource utilization.
Uniformity Distribution Coefficient
The Uniformity Distribution Coefficient (UDC) measures the evenness of water application in a sprinkler irrigation system. It is calculated based on catch data from a uniformity test. A higher UDC indicates better water distribution uniformity, with values above 85% considered optimal. Factors such as nozzle size, operating pressure, and sprinkler spacing significantly influence UDC. Ensuring high uniformity is critical for crop health and water conservation, as uneven distribution can lead to overwatering or underwatering in specific areas. Regular testing and adjustments are essential to maintain optimal system performance and efficiency.
Evaluation of Application Rates and Efficiency

Evaluating application rates and efficiency in sprinkler irrigation systems involves assessing water delivery and ensuring optimal crop water use. Key factors include nozzle size, operating pressure, and soil infiltration rates. Tools like flow meters and soil moisture sensors help measure application rates and identify inefficiencies. Proper evaluation ensures water is applied uniformly, minimizing waste and runoff. This process is crucial for maintaining system performance, reducing operational costs, and promoting sustainable water use in agriculture.
Optimizing Sprinkler System Performance
Optimizing sprinkler system performance involves regular maintenance, proper nozzle sizing, and pressure adjustments to ensure uniform water distribution. Adjusting sprinkler spacing and alignment based on soil type and crop requirements enhances efficiency. Automation and smart sensors can monitor and control water application, reducing waste. Seasonal inspections of pipes and sprinkler heads help identify and repair leaks or clogs. By fine-tuning these elements, sprinkler systems achieve better water conservation, reduced energy costs, and improved crop yields, ensuring long-term agricultural productivity and sustainability.

Economic Considerations in System Design
Economic considerations in sprinkler system design balance initial installation costs with long-term water and energy savings, ensuring sustainable agricultural practices and resource efficiency.
Cost Analysis of Sprinkler System Components
A cost analysis of sprinkler system components involves evaluating expenses for pipes, sprinklers, pumps, and control systems. Initial investment varies based on material quality, system size, and water source. Permanent systems with buried lines are more costly but durable, while portable systems offer flexibility at lower costs. Long-term savings from water efficiency and reduced labor often offset initial expenditures, making sprinkler irrigation a cost-effective solution for sustainable agriculture and water resource management.
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Water Savings
While the initial investment in a sprinkler irrigation system can be substantial, long-term water savings often justify the cost. Efficient systems reduce water waste through precise application and uniform distribution, lowering overall consumption. Over time, these savings can offset the initial expenditure, making the system economically viable. Additionally, improved crop yields and reduced labor costs further enhance the system’s profitability, emphasizing the importance of balancing upfront costs with sustainable, long-term benefits in irrigation system design;
Economic Benefits of Efficient Irrigation
Efficient sprinkler irrigation systems offer significant economic benefits, including increased crop yields and improved water conservation. By minimizing water waste and optimizing application rates, farmers can reduce operational costs while maintaining or enhancing productivity. Additionally, efficient systems often lead to lower energy consumption and extended equipment lifespan, further cutting expenses. These savings, combined with potential increases in crop quality and market value, make efficient irrigation a sound long-term investment for agricultural and landscape management applications.
The design of sprinkler irrigation systems plays a crucial role in enhancing water conservation and agricultural productivity. By optimizing factors like nozzle size, spacing, and pressure, these systems ensure efficient water distribution, reducing waste and energy costs. Adoption of efficient irrigation practices aligns with environmental and economic goals, promoting sustainable farming. Whether for small-scale gardens or large agricultural fields, well-designed sprinkler systems offer long-term benefits, making them a vital tool for modern agriculture and water resource management.

